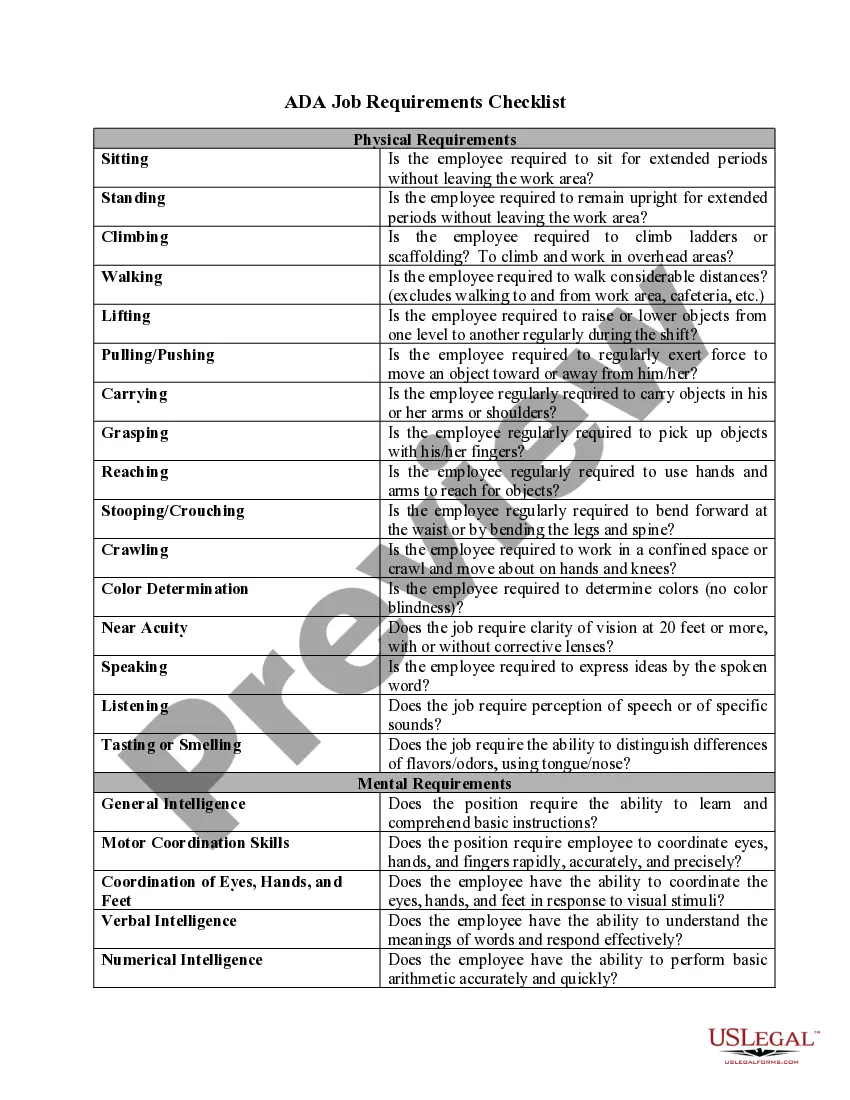
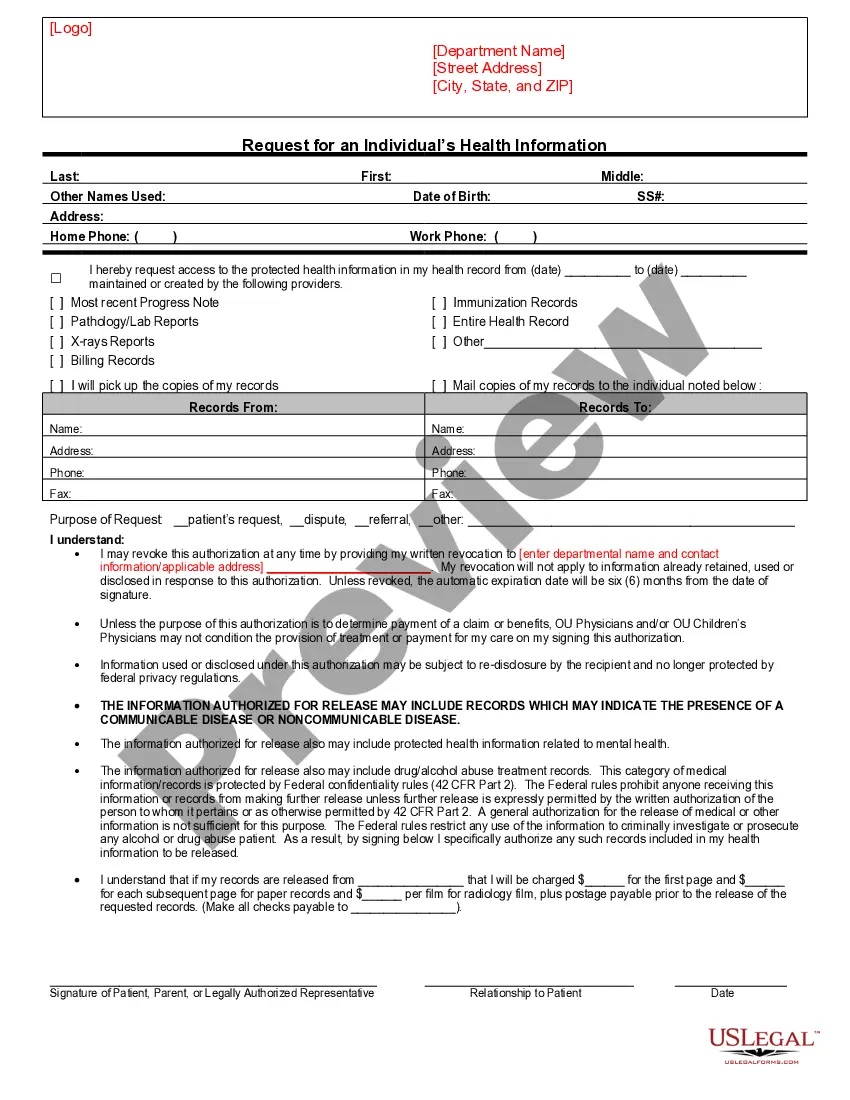
The Chicago Illinois Digital Signature Ordinance, also known as Signaturverordnung or Sign, is a significant legal regulation put in place by the city of Chicago, Illinois, to govern the use and validity of digital signatures within various domains. This ordinance aims to provide a secure and efficient method for conducting electronic transactions and ensuring their authenticity. Digital signatures, as defined in the Chicago Illinois Digital Signature Ordinance, are electronic signatures encrypted with the intent to authenticate the identity of the signatory and verify the integrity of the electronic document being signed. By utilizing cryptographic techniques, digital signatures offer a reliable means to establish non-repudiation, meaning the signer cannot deny their involvement in the transaction later on. The Signaturverordnung (Sign) outlines the requirements and processes for legally binding digital signatures in Chicago, Illinois. It sets the standards and guidelines for implementing secure digital signature technologies, specifying the encryption algorithms, cryptographic key management, and security protocols to be utilized. Under the Chicago Illinois Digital Signature Ordinance — Signaturverordnun— - SigV, there exist distinct types of digital signatures, each serving different purposes: 1. Basic Digital Signatures: These are the most commonly used digital signatures and are employed across various industries. Basic digital signatures ensure the integrity and authenticity of the electronically signed documents by applying cryptographic techniques and verifying the signer's identity. 2. Advanced Digital Signatures: Advanced digital signatures offer an enhanced level of security and additional features beyond basic signatures. They may incorporate techniques such as timestamping, which provides evidence that the document existed at a specific point in time, adding an extra layer of trust and preventing document tampering. 3. Qualified Digital Signatures: Qualified digital signatures meet the highest standards of security and legal validity. These signatures are created using qualified electronic signatures (YES) and require a qualified digital certificate issued by accredited certification authorities. Qualified digital signatures are legally equivalent to handwritten signatures and hold significant legal weight in court. By implementing the Chicago Illinois Digital Signature Ordinance — Signaturverordnun— - SigV, the city of Chicago aims to foster a secure and reliable environment for electronic transactions, enabling businesses, government agencies, and individuals to conduct legal and binding electronic operations while minimizing the risks associated with fraudulent activities and document forgery.
Chicago Illinois Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV
Description
How to fill out Chicago Illinois Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV?
Dealing with legal forms is a must in today's world. Nevertheless, you don't always need to seek qualified assistance to draft some of them from scratch, including Chicago Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV, with a platform like US Legal Forms.
US Legal Forms has more than 85,000 forms to pick from in various categories ranging from living wills to real estate papers to divorce papers. All forms are arranged according to their valid state, making the searching experience less challenging. You can also find detailed resources and guides on the website to make any activities associated with document completion straightforward.
Here's how to purchase and download Chicago Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV.
- Go over the document's preview and description (if available) to get a general idea of what you’ll get after downloading the document.
- Ensure that the document of your choice is adapted to your state/county/area since state regulations can affect the validity of some documents.
- Examine the related forms or start the search over to find the right file.
- Hit Buy now and register your account. If you already have an existing one, choose to log in.
- Choose the option, then a suitable payment gateway, and purchase Chicago Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV.
- Choose to save the form template in any offered format.
- Go to the My Forms tab to re-download the file.
If you're already subscribed to US Legal Forms, you can find the appropriate Chicago Digital Signature Ordinance - Signaturverordnung - SigV, log in to your account, and download it. Needless to say, our website can’t replace a legal professional entirely. If you need to cope with an extremely difficult case, we advise getting a lawyer to check your form before signing and submitting it.
With over 25 years on the market, US Legal Forms became a go-to platform for various legal forms for millions of customers. Become one of them today and get your state-specific paperwork with ease!