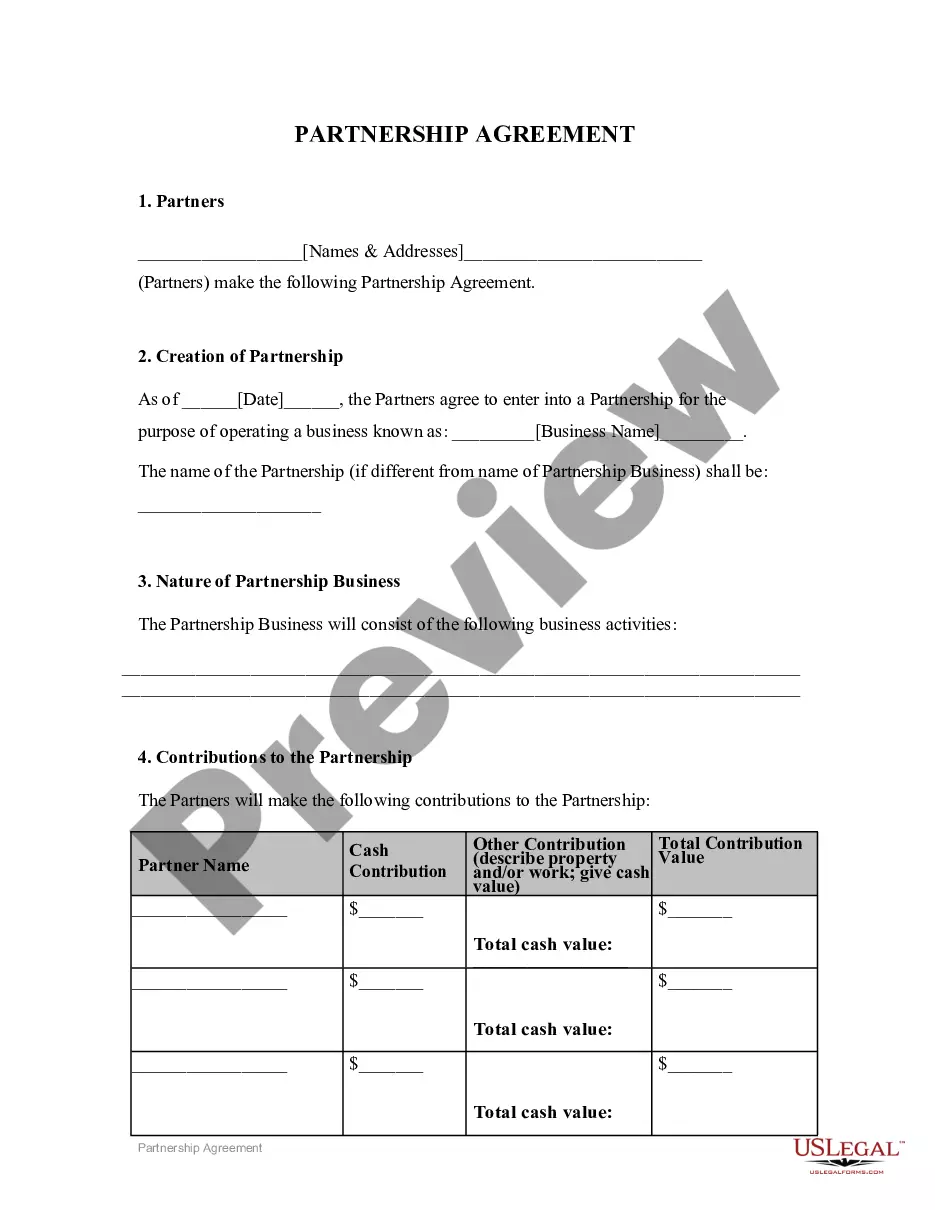
This is a corporate policy document designed to meet the standards of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, a provision of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934. FCPA generally prohibits payments by companies and their representatives to foreign (i.e., non-U.S.) government and quasi-government officials to secure business.
Los Angeles California Foreign Corrupt Practices Act — Corporate Policy is a set of guidelines specifically designed to prevent US companies or individuals from engaging in corrupt practices while conducting business with foreign entities. The Los Angeles California Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (CPA) Corporate Policy aims to ensure transparency, maintain ethical standards, and prevent bribery and corruption in international business transactions. Under the Los Angeles California Foreign Corrupt Practices Act — Corporate Policy, there are various types of policies that organizations can implement to comply with the CPA regulations. These policies include: 1. Anti-Bribery Policy: This policy outlines the organization's commitment to refrain from offering, promising, or providing any form of bribe, kickback, or improper benefit to foreign officials, including individuals from governmental bodies or international organizations. 2. Compliance and Due Diligence Policy: This policy requires companies to undertake proper due diligence procedures before entering into business relationships with foreign entities. It ensures that organizations are aware of the potential risks and reputational damage associated with dealing with corrupt partners. 3. Gifts and Entertainment Policy: To ensure that gifts, entertainment, or hospitality provided by the company to foreign officials or business partners comply with the CPA, this policy sets specific limitations, reporting requirements, and approval processes for such activities. 4. Third-Party Risk Management Policy: This policy focuses on mitigating risks arising from working with third-party agents, consultants, or intermediaries. It establishes rigorous vetting procedures, contractual obligations, and monitoring mechanisms to prevent any illegal or corrupt practices by these entities. 5. Record-Keeping and Internal Controls Policy: This policy emphasizes the importance of accurate record-keeping and maintaining effective internal controls. It ensures that all financial transactions and interactions with foreign officials are properly documented, transparent, and subject to review. 6. Training and Awareness Policy: To promote CPA compliance throughout the organization, this policy outlines mandatory training sessions and awareness campaigns to educate employees on ethical business practices, CPA requirements, and the consequences of non-compliance. Implementing and adhering to the Los Angeles California Foreign Corrupt Practices Act — Corporate Policy is crucial for companies operating internationally, as violations can lead to severe legal consequences, including criminal charges, fines, and reputational damage. Therefore, organizations must tailor their policies to suit their specific operations, risk profiles, and industry sectors while staying true to the CPA's underlying guidelines.Los Angeles California Foreign Corrupt Practices Act — Corporate Policy is a set of guidelines specifically designed to prevent US companies or individuals from engaging in corrupt practices while conducting business with foreign entities. The Los Angeles California Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (CPA) Corporate Policy aims to ensure transparency, maintain ethical standards, and prevent bribery and corruption in international business transactions. Under the Los Angeles California Foreign Corrupt Practices Act — Corporate Policy, there are various types of policies that organizations can implement to comply with the CPA regulations. These policies include: 1. Anti-Bribery Policy: This policy outlines the organization's commitment to refrain from offering, promising, or providing any form of bribe, kickback, or improper benefit to foreign officials, including individuals from governmental bodies or international organizations. 2. Compliance and Due Diligence Policy: This policy requires companies to undertake proper due diligence procedures before entering into business relationships with foreign entities. It ensures that organizations are aware of the potential risks and reputational damage associated with dealing with corrupt partners. 3. Gifts and Entertainment Policy: To ensure that gifts, entertainment, or hospitality provided by the company to foreign officials or business partners comply with the CPA, this policy sets specific limitations, reporting requirements, and approval processes for such activities. 4. Third-Party Risk Management Policy: This policy focuses on mitigating risks arising from working with third-party agents, consultants, or intermediaries. It establishes rigorous vetting procedures, contractual obligations, and monitoring mechanisms to prevent any illegal or corrupt practices by these entities. 5. Record-Keeping and Internal Controls Policy: This policy emphasizes the importance of accurate record-keeping and maintaining effective internal controls. It ensures that all financial transactions and interactions with foreign officials are properly documented, transparent, and subject to review. 6. Training and Awareness Policy: To promote CPA compliance throughout the organization, this policy outlines mandatory training sessions and awareness campaigns to educate employees on ethical business practices, CPA requirements, and the consequences of non-compliance. Implementing and adhering to the Los Angeles California Foreign Corrupt Practices Act — Corporate Policy is crucial for companies operating internationally, as violations can lead to severe legal consequences, including criminal charges, fines, and reputational damage. Therefore, organizations must tailor their policies to suit their specific operations, risk profiles, and industry sectors while staying true to the CPA's underlying guidelines.